Dog Age Calculator
Convert your dog's age to human years and understand their life stage
Human Years
Life Stage
Understanding Dog Ages
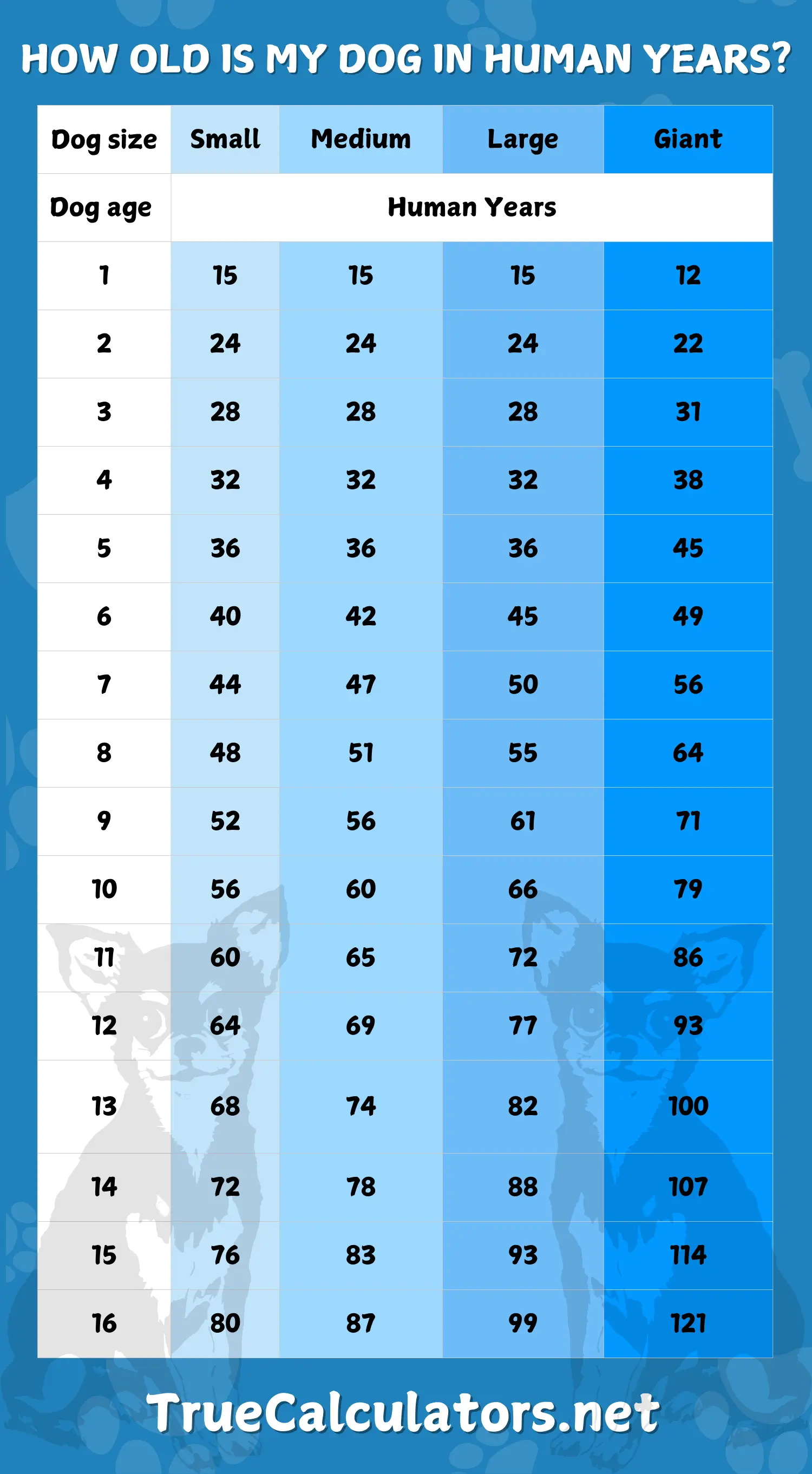
Dogs age much faster than humans, with significant variations based on their size and breed. The first year of a dog's life equals approximately 15 human years, while the second year adds another 9 years (totaling 24 human years by age 2). After age 2, the aging rate depends on size: small dogs age about 4 years per dog year, medium dogs 5 years, large dogs 6 years, and giant breeds 7 years per dog year. This size-dependent aging pattern reflects a biological phenomenon where larger dogs have shorter lifespans than smaller dogs. Understanding your dog's life stage helps provide age-appropriate care, nutrition, exercise, and medical attention to ensure they live their healthiest, longest life possible.
Dog Life Stages by Size
Small Dogs (up to 20 lbs)
- Puppy (0-1 year): Rapid growth, teething, socialization critical
- Adolescent (1-2 years): High energy, training continues, sexual maturity
- Adult (3-6 years): Prime years, stable temperament, peak health
- Mature (7-10 years): Middle age, may show subtle aging signs
- Senior (11-14 years): Slower pace, possible health issues, needs adjustments
- Geriatric (15+ years): Advanced age, special care needed
Medium Dogs (21-50 lbs)
- Puppy (0-1 year): Growth and socialization phase
- Adolescent (1-2 years): Energy and training
- Adult (3-6 years): Prime physical condition
- Mature (7-9 years): Middle age begins earlier than small breeds
- Senior (10+ years): Aging signs more apparent
Large & Giant Dogs (50+ lbs)
- Puppy (0-2 years): Longer growth period, joint care critical
- Adult (3-5 years): Peak years, shorter than small breeds
- Senior (6-8+ years): Aging begins much earlier, proactive health monitoring essential
- Giant breeds often age fastest and have shortest lifespans (8-10 years typical)
Signs of Aging in Dogs
Physical Changes
- • Graying muzzle and face
- • Cloudy eyes (nuclear sclerosis or cataracts)
- • Weight gain or muscle loss
- • Dental disease and bad breath
- • Dry, thinning coat
- • Lumps and bumps on skin
- • Reduced stamina and endurance
Behavioral Changes
- • Sleeping more, less active
- • Confusion or disorientation (cognitive dysfunction)
- • Anxiety or restlessness at night
- • House training accidents
- • Reduced interest in play or walks
- • Changes in social interaction
- • Increased vocalization
Health Indicators
- • Arthritis and joint stiffness
- • Difficulty getting up or lying down
- • Hearing loss
- • Vision problems
- • Increased thirst or urination
- • Digestive issues
- • Heart or kidney problems
Mobility Changes
- • Reluctance to jump or climb stairs
- • Stiffness after rest
- • Slower walking pace
- • Difficulty on slippery floors
- • Reduced flexibility
- • Limping or favoring limbs
- • Reluctance to exercise
Dog Health and Care Throughout Life
Dogs are social pack animals that thrive on companionship, structure, and mental stimulation. They require daily exercise appropriate to their age, breed, and energy level. Puppies need extensive socialization during their critical period (3-14 weeks) to develop into well-adjusted adults. Dogs communicate primarily through body language, vocalizations, and scent. Regular veterinary care including vaccinations, parasite prevention, and dental cleanings is essential for longevity. Spaying/neutering provides health benefits and prevents unwanted behaviors. Senior dogs benefit from twice-yearly vet visits to catch age-related problems early. Proper nutrition, exercise, mental enrichment, and preventive care can significantly extend a dog's healthy years.
Essential Dog Care Requirements:
- Provide high-quality dog food appropriate for life stage, size, and activity level
- Ensure constant access to fresh, clean water
- Daily exercise tailored to breed, age, and health (walks, play, mental stimulation)
- Annual veterinary wellness exams (twice yearly for seniors), vaccinations, parasite prevention
- Spay/neuter to prevent health issues and behavioral problems (unless breeding responsibly)
- Early and ongoing socialization with people, dogs, and various environments
- Positive reinforcement training for obedience and good manners
- Regular grooming: brushing, nail trims, ear cleaning, bathing as needed
- Dental care: brushing, dental chews, professional cleanings to prevent disease
- Safe, comfortable shelter and sleeping area indoors
- Mental enrichment through puzzle toys, training, sniffing activities, social interaction
- Microchip and ID tags for identification if lost
- Protection from extreme temperatures - never leave in hot cars
- Monitor weight to prevent obesity-related health problems
- For seniors: orthopedic beds, ramps/steps, adjusted exercise, more frequent vet care
Common Dog Health Considerations
Arthritis & Joint Disease
Extremely common in senior and large breed dogs. Degenerative joint disease causes pain, stiffness, difficulty moving. Signs include reluctance to jump, slower gait, stiffness after rest. Manageable with weight control, joint supplements, pain medication, physical therapy. Large breeds prone to hip/elbow dysplasia requiring early intervention.
Dental Disease
Affects 80% of dogs over age 3. Plaque and tartar buildup leads to gingivitis, tooth loss, painful infections. Bacteria can spread to heart, liver, kidneys causing serious problems. Prevention through regular brushing, dental chews, professional cleanings. Signs include bad breath, drooling, reluctance to eat hard food, pawing at mouth.
Obesity
Over 50% of dogs are overweight or obese. Excess weight causes arthritis, diabetes, heart disease, reduced lifespan. Prevention through portion control, healthy treats, regular exercise. Monitor body condition - should feel ribs easily, see waist from above. Weight loss requires veterinary guidance for safe, gradual reduction.
Cognitive Dysfunction Syndrome
Age-related mental decline similar to Alzheimer's in humans. Signs include disorientation, sleep-wake cycle changes, house soiling, reduced interaction, staring at walls. Affects 14-35% of senior dogs. Manageable with medications, mental enrichment, consistent routine, environmental modifications. Early recognition improves quality of life.
Latest Scientific Research on Dog Aging
UC San Diego Epigenetic Clock Study (2019)
Groundbreaking research analyzed DNA methylation patterns in Labrador Retrievers to understand biological aging. The study revealed that dogs age rapidly in their first few years (comparable to a human teenager by age 1), then aging slows dramatically. This explains why traditional "multiply by 7" is inaccurate.
Scientific Formula:
Human age = 16 × ln(dog age) + 31
(where ln is the natural logarithm)
Examples:
- • A 1-year-old dog: 16 × ln(1) + 31 = 31 human years
- • A 2-year-old dog: 16 × ln(2) + 31 = 42 human years
- • A 5-year-old dog: 16 × ln(5) + 31 = 57 human years
- • A 10-year-old dog: 16 × ln(10) + 31 = 68 human years
Size and Longevity Research
Multiple studies have confirmed that larger dogs age faster and have shorter lifespans. Giant breeds (Great Danes, Mastiffs) typically live 8-10 years, while small breeds (Chihuahuas, Toy Poodles) often live 14-16 years or more. This phenomenon is unique among mammals - usually larger animals live longer. Theories include faster cellular aging, higher rates of cancer, and increased oxidative stress in larger dogs.
References
The lifespan and care data used in this calculator are based on scientific research from reputable sources:
Dog Age Chart
Related Calculators
Note: This calculator provides estimates based on size-specific aging patterns and scientific research. Individual dog aging varies significantly based on breed, genetics, lifestyle, diet, exercise, veterinary care, and overall health management. Small breeds typically live 12-16 years, medium breeds 10-13 years, large breeds 8-12 years, and giant breeds 7-10 years. Mixed breed dogs often live longer than purebreds due to genetic diversity. These estimates assume proper care with quality nutrition, regular veterinary attention, appropriate exercise, and preventive health measures. Consult with your veterinarian for specific health and age-related guidance for your dog.
Recommended Calculator

Casio FX-991ES Plus
The professional-grade scientific calculator with 417 functions, natural display, and solar power. Perfect for students and professionals.
View on Amazon